Roasted Saffron
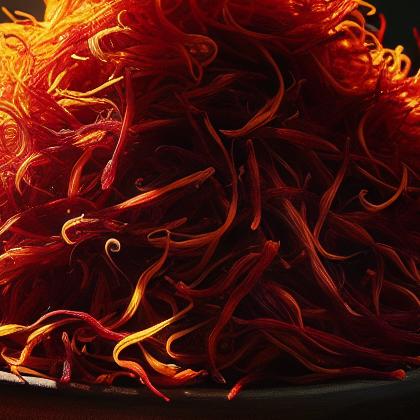
Saffron (pronounced /ˈsæfrən/ or /ˈsæfrɒn/)is a spice derived from the flower of Crocus sativus, commonly known as the "saffron crocus". Saffron crocus grows to 20–30 cm (8–12 in) and bears up to four flowers, each with three vivid crimson stigmas, which are the distal end of a carpel.The styles and stigmas, called threads, are collected and dried to be used mainly as a seasoning and colouring agent in food. Saffron, long among the world's most costly spices by weight, is native[dubious – discuss] to Greece or Southwest Asia and was first cultivated in Greece.As a genetically monomorphic clone, it was slowly propagated throughout much of Eurasia and was later brought to parts of North Africa, North America, and Oceania.
Roasted saffron Pairs With:

Roasted saffron Properties:
| Food Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Flavor Profile | Bitter | Roasted saffron has a slightly bitter taste due to the natural compounds present in saffron. |
| Umami | Roasted saffron offers a savory and rich flavor profile that enhances the overall taste of dishes. | |
| Texture | Dryness | Roasted saffron has a dry texture, making it easy to crush and mix into dishes. |
| Nutritional Value | Phytochemicals | Roasted saffron contains phytochemicals such as crocin and safranal, which contribute to its health benefits and unique flavor. |
| Color | Natural Pigments | Roasted saffron exhibits a deep red color due to the natural pigments present in saffron threads. |
| Aroma | Volatile Compounds | Roasted saffron releases volatile compounds that give it a distinctive aroma and flavor when added to dishes. |
Food Pairing App - Version 1.2.0
